Introduction to wide area networks (WAN): Concepts and applications
Understanding the infrastructure that keeps us connected is crucial. Among these technologies, Wide Area Networks (WAN) play a pivotal role in bridging vast distances, enabling seamless communication across cities, states, and even nations.
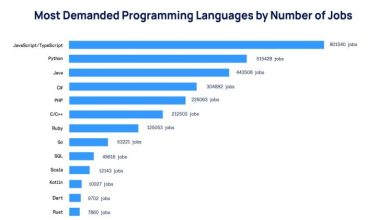
Importance of WAN (Wide Area Networks) – Read on to understand why it is crucial for your business.
Ø Economic efficiency
By allowing centralised data centres and cloud services, WANs help organisations reduce operational costs.
Ø Resource sharing
They enable the sharing of resources and data among offices, educational institutions, and government bodies located in different parts of the country.
Ø Connectivity across distances
WANs enable communication over huge geographical areas, which is critical in today’s varied and distant countries.
Ø Improved communication
WANs are critical for real-time communication, as they enable services such as video conferencing and VoIP, which are essential for both corporate and personal interactions.
Ø Scalability
WANs provide the capacity to scale operations, which is critical for enterprises trying to increase their reach in India and beyond.
Ø Support for mobile users
They provide critical connections for mobile users and remote workers, hence promoting India’s booming gig economy and flexible work environments.
What is WAN?
A Wide Area Network (WAN) is a telecommunications network which extends over a large geographical area for the primary purpose of computer networking. Unlike networks that operate within a confined space, WANs cover broad areas that can range from a state to an entire country or continent.
Difference between LAN and WAN or LAN vs WAN – All you must know about it
Ø Geographical area
LANs are restricted to a small area like a single building or campus, whereas WANs cover larger areas, often spanning multiple locations.
Ø Speed
LANs typically offer higher data transfer speeds due to their localised nature, while WANs may experience slower speeds due to the vast distances involved.
Ø Ownership
LANs are usually owned, controlled, and managed by a single organisation or individual. In contrast, WANs might involve multiple telecommunications providers and infrastructures.
Ø Cost
Due to the size and technology necessary to connect distant sites, WANs are often more expensive to set up and operate than LANs.
Ø Technology utilised
LANs often employ Ethernet and Wi-Fi, whereas WANs use MPLS, ATM, Frame Relay, and, more recently, SD-WAN.
Concepts of WAN
Ø MPLS (Multi-Protocol Label Switching)
Labelling packets makes it easier to route data efficiently, which is critical for traffic management.
Ø Software-defined WAN (SD-WAN)
Uses software to handle internet access and services, providing a more flexible and cost-effective solution.
Ø VPN (Virtual Private Network)
Provides secure communication across a public network, which is critical for distant workers and enterprises.
Ø Leased lines
Dedicated, private communication lines rented for WAN connectivity, offering reliability for critical operations.
Ø Satellite communication
Provides WAN connectivity in remote areas where traditional infrastructure is not feasible.
Ø Fiber optics
Offers high-speed data transmission across long distances, supporting the backbone of India’s internet.
Ø Hybrid WAN
Combines multiple connection types (like MPLS, broadband, and cellular) for cost efficiency and reliability.
Ø Cloud networking
Leverages cloud services for WAN purposes, offering scalability and flexibility for businesses.
Ø Quality of service or QoS
Ensures performance standards for traffic over WAN, critical for voice and video communication.
Applications of WAN
Ø E-governance
WAN plays a critical role in the implementation of e-governance initiatives across India, aiming to make government services more accessible to the general population. By connecting government offices across different levels (central, state, and local), WAN enables the seamless exchange of information and the efficient delivery of public services online. This digital transformation includes services like filing taxes, obtaining licenses, and registering property. E-Governance via WAN improves transparency, lowers corruption, and streamlines government procedures, all of which benefit residents nationally.
Ø Healthcare
WAN is altering healthcare by providing telemedicine services, including distant consultations, diagnosis, and treatment. This is critical in a country with a considerable urban-rural disparity in healthcare access. Telemedicine allows patients in rural places to consult with specialists in urban centres without having to travel. WAN enables the transfer of medical data, such as test results and medical imaging, as well as real-time video consultations, increasing access to expert care and relieving demand on urban healthcare facilities.
Ø Telecommuting
Telecommuting, assisted by WAN, enables people to operate from anywhere, breaking down conventional boundaries of distance and geographical isolation. This flexibility is especially useful in a nation with large urban-rural divisions and varied degrees of infrastructural development. Businesses that use WAN may access a larger talent pool, save money on office space, and help their workers maintain a work-life balance. Enhanced WAN solutions provide safe and dependable connectivity to corporate networks, facilitating collaboration via video conferencing, cloud services, and virtual desktops.
Ø Banking and finance
In the banking and finance industry, WAN enables branch connection and safe transactions across India, supporting the country’s financial inclusion aspirations. Banks can provide consistent services nationally by linking rural and urban branches over WAN, such as online banking, financial transfers, and digital payments. This link guarantees that financial services are accessible to the unbanked and underbanked, boosting economic inclusion and growth. Secure WAN solutions safeguard the secrecy and integrity of financial transactions, which is critical for preserving consumer confidence.
Ø Retail
In the retail industry, WANs support Point of Sale (POS) systems and inventory management across several locations. Retail businesses employ WAN to connect their locations across the country, allowing for centralised control of sales data, inventory, and customer information. This connection guarantees that inventory levels are adjusted, sales data is updated in real time, and customers have a consistent shopping experience across all locations.
Final thoughts
Understanding WAN and its applications is critical to realising the full potential of digital India. From enhancing connection to boosting economic growth, the importance of WAN in influencing the future cannot be emphasised. As technology advances, so will the possibilities and uses of WAN, offering an even more connected and efficient future.